For this purpose experts from the Vancouver General Hospital, Canada attempted to use dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) for diagnosing this disease in patients. These experts were believed to have used Siemens’ SOMATOM Definition computed tomography in this study. Together all these experts were believed to have developed a dual-energy algorithm for detecting the crystals of uric acid.
Accurately diagnosing gout may be a little complicated because its symptoms may be akin to those of arthritis. The use of this new technique of accurately diagnosing gout is believed to have attracted a lot of attention in Canada. It was stated that the high sensitivity of the DECT technique may be able to identify the deposits of uric acid crystals.
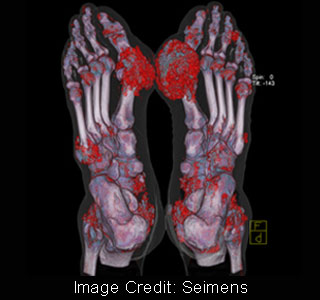
Seimens’ SOMATOM Definition is believed to be the only CT scanner in the world to feature two X-ray tubes, which may be capable of producing different energies simultaneously. By conducting scans at different energies, it became possible to verify the attenuation values of the uric acid crystals. Further by color coding these attenuation’s the experts could identify the uric acid crystals on the scan image.
Dr. Savvas Nicolaou, Director of Emergency Radiology at Vancouver General Hospital and Associate Professor at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, says that, “Our findings indicate that deposits of mono sodium urate crystals can be detected sub clinically more efficiently using DECT than with the traditional clinical examination.â€
Apart from this, Dr. Nicolaou also states that, “To our surprise, the study showed that uric acid can be initially deposited in tendons and ligaments near and within the knee joint, ankle joint, wrist, ie in the collateral ligament / cruciate ligament and deep flexor tendons of the wrist.â€
This information could be very crucial because such deposits are believed to increase the likelihood of tendons and ligaments for tears. Therefore by early detection of the disease in its initial stages itself, it may be possible to prevent the damage incurred to tendons and ligaments.
