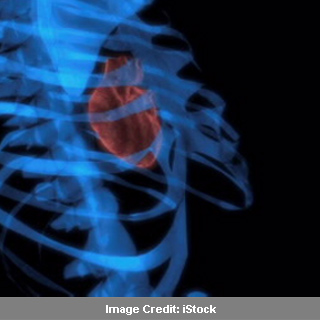
The novel agent is not only inexpensive, but also more effective. It allegedly stays in the body long enough to image many different organs. The tantalum oxide nanoparticles for CT appear particularly beneficial for physicians treating patients diagnosed with heart disease and breast cancer.
While detecting nanoparticles that are non-toxic, scientists tested large batches of tantalum oxide nanoparticles. These agents probably exhibited ‘remarkable performances’ during imaging tests of the heart, lymph nodes, kidneys, and other structures in laboratory rats. It was observed that the nanoparticles may not affect normal functioning of organs. Taeghwan Hyeon and colleagues note that these particles have great importance while checking blood vessels in the heart for blockages, and lymph nodes for the spread of breast cancer.
The research was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
